According to a recent report by Delphi Digital, the main value drivers for Bitcoin are its ability to serve as a censorship-resistant store of value
as well as offer the world a viable alternative to government-backed currencies
.
2/ We believe the primary long-term value drivers for $BTC revolve around its ability to serve as 1) a censorship-resistant store of value and 2) a “check” on governments as an alternative, country-agnostic digital reserve currency. pic.twitter.com/C6VwbqceQh
— Delphi Digital (@Delphi_Digital) December 10, 2018
The New York-based digital research company analysed the current use cases of Bitcoin and identified opportunities for growth. At the same time, the report presents an in-depth analysis of the potential risks associated with cryptocurrencies and offers solutions to mitigate them.
The report acknowledges that Bitcoin is a valid option for investors who want to protect their assets. In the authors’ opinion:
The key characteristics of bitcoin (censorship resistance, verifiable ownership, immutability, etc.) make it an attractive alternative to today’s instruments for hedging against inflation or storing one’s wealth without the risk of seizure.
Bitcoin’s Legality Around the World
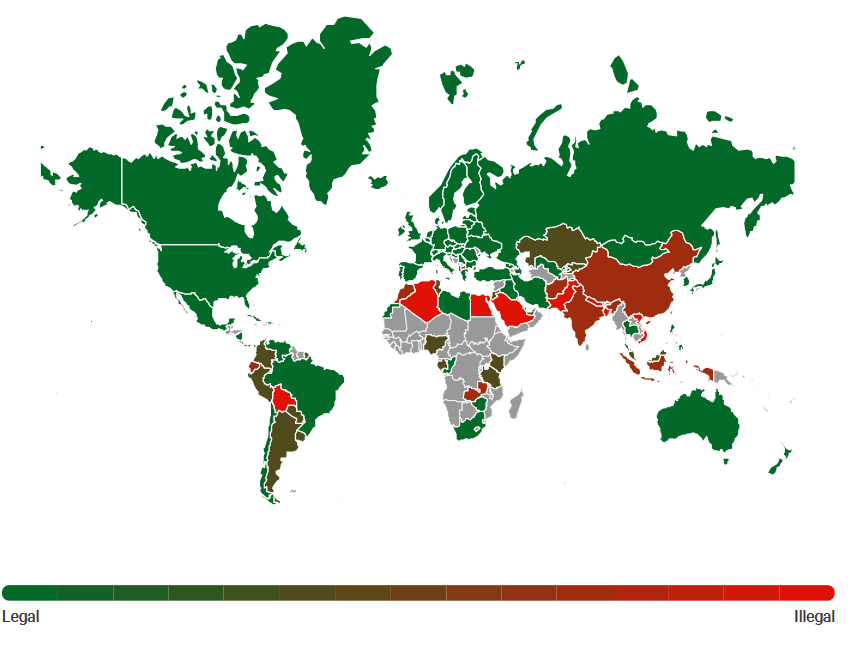
The Delphi report presents a detailed look at the current status of the first cryptocurrency all over the world. Apart from 10 countries, Bitcoin is legal throughout the world. However, different countries view cryptocurrency differently.
For example:
- The US IRS classified Bitcoin as commodity (and not as a currency) and recently issued guidance on its taxation;
- Japan has recognised it as a form of payment since March 2017;
- South Korea recognised Bitcoin exchanges as legal as long as they register with the local financial authorities;
- All the European countries recognise Bitcoin as a legal tender, even though each of them has a different view on the classification.
From 1 July 2017, Australia started treating cryptocurrency “just like money“, and it is no longer subject to double taxation.
The countries that do not consider Bitcoin legal are mostly in South-East Asia, the Middle East, North Africa and South America.
A Potential Solution for Developing Economies
The nature of Bitcoin – free of the control of central bank and other traditional financial institutions – makes it a good choice for vulnerable economies. Using the examples of Venezuela and Argentina, the Delphi researchers show that the cryptocurrency is a good alternative to volatile fiat currencies.
Since Bitcoin is not valued against the socio-political stability of any particular country, people may rely on it to protect their assets and investments. Apart from this, the researchers found other strong points in favour of the cryptocurrency as a solution for developing economies:
- It is accessible even to people who do not hold a bank account;
- Using Bitcoin reduces transaction fees for frequent remittances;
- It gives people direct ownership over their wealth, free of intermediaries (central banks)
- Transactions are faster.
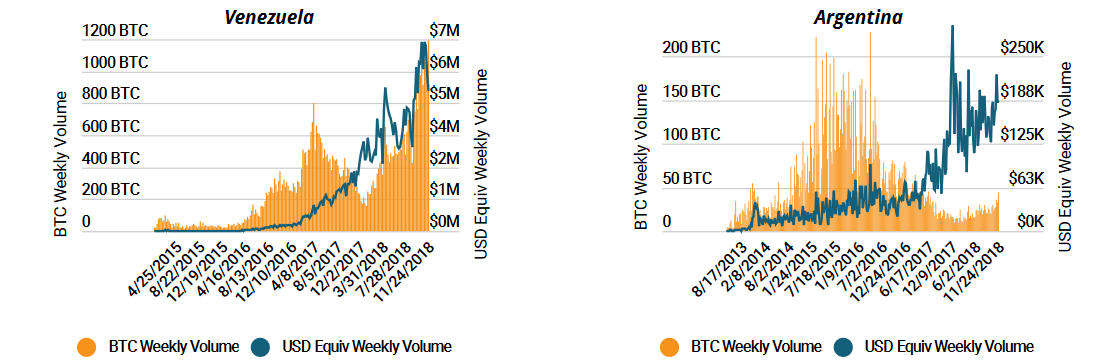
Aside from being a solution for the unbanked, the report also sees Bitcoin succeeding at becoming a ubiquitous form of payment over the internet
.
Key Advantages of Bitcoin over Established Stores of Value
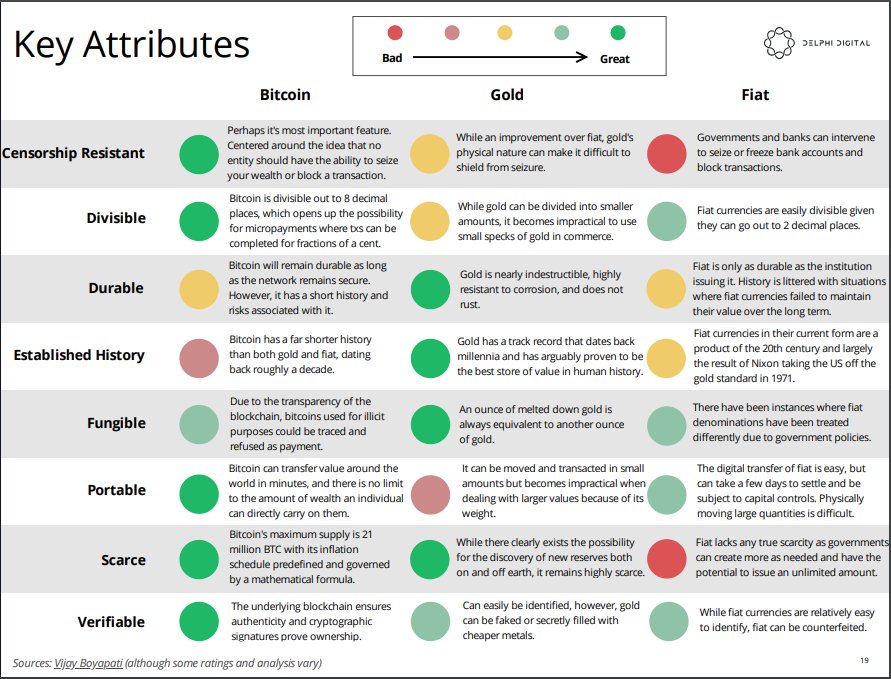
In a different section, the Delphi report compares Bitcoin against the traditional stores of value: gold and fiat currencies. The authors used the key characteristics that define a store of value and found that Bitcoin performs well for most of them.
These are:
- Censorship resistance – Bitcoin is not controlled by any entity that could seize it or block a transaction;
- Divisibility – BTC can be divided out to 8 decimal places, allowing micropayments;
- Portability – users can perform transfers within minutes around the world and there are no limitations on the maximum amount;
- Scarcity – the maximum supply of Bitcoin is 21 million BTC at global level;
- Verifiability – blockchain technology guarantees the authenticity and encrypted signatures are proofs of ownership.
Key Risks Associated with Bitcoin
Being only 10 years old, there are, naturally, still some risks associated with Bitcoin. Along with 11 current risks and concerns, the report also presents their mitigants. Some of the risks the authors identified are for instance:
Scalability issues
Bitcoin’s scalability problem is well-known. However, the community is always working on developing new scaling solutions. One of the most important ones, according the report, is the Lightning Network.
Volatility
The price of Bitcoin is continually fluctuating. However, the authors expect the historical volatility of Bitcoin to decline as the broader crypto market matures
. And what will drive the maturation is the gradual adoption among both individual and institutional participants.
Hackers & protocol bugs
So far, three major vulnerabilities occurred in the Bitcoin ecosystem: a DDOS attack in 2018, two software versions operating simultaneously in 2013 and a value overflow incident in 2010. But, as the report states, As seen throughout its history, when there is a bug it is usually identified and patched quickly.
PoW energy consumption
Bitcoin is a heavy consumer of electricity, with a strong impact on the environment. However, miners and mining farms are already looking into environmental-friendly alternatives, such as using clean energy.
Mining centralisation
Due to cheap energy, over 68% of Bitcoin mining pools are located in China, which presents a potential threat to network security. Another concern is the large amount of control that one specific company potentially has over the network. The authors, though, mention that Game theory, among other factors, comes into play and suggests that these mining pools would also not kill their golden goose.
Sustainability without block reward
The Bitcoin block mining reward (the reward eligible miners get for each block they mine successfully) halves every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every 4 years. The reward is currently 12.5 BTC, but with the next halving it will decrease to 6.25 BTC. And eventually, sometime around the year 2140, will diminish to 0. As the report explains, At a certain point, fees will have to sustain the network by providing an economic incentive for miners.